What Is a Mind Map and How to Use It to Learn Anything
Mind map learning is a powerful technique that helps people understand and retain information more effectively. Whether someone is a student, professional, or lifelong learner, mind mapping offers a visual approach to organizing knowledge that can be adapted to any subject. This blog post explains what a mind map is and how to use it as a tool for learning virtually anything.
What Is a Mind Map?
A mind map is a visual diagram used to represent ideas, concepts, or information. It starts with a central theme or topic placed in the middle of a blank page. From there, related ideas branch outward like the limbs of a tree. Each branch can further split into sub-branches, creating a structure that mirrors the brain’s natural way of processing and storing data.
Unlike traditional note-taking, which is often linear and text-heavy, mind maps use keywords, symbols, images, and colors to stimulate memory and creativity. This visual and non-linear format makes it easier for learners to see connections between ideas and to recall information more easily.
Why Mind Mapping Works
Mind mapping taps into both sides of the brain — logical and creative. It allows learners to organize information in a way that feels intuitive, often leading to deeper comprehension and longer retention. By combining visual elements and hierarchical thinking, the mind map becomes both a learning aid and a creative brainstorming tool.
Research has shown that mind mapping can enhance memory, improve problem-solving skills, and boost productivity. It’s particularly helpful for visual learners, but it can benefit anyone looking to grasp complex topics more clearly.
How to Create a Mind Map
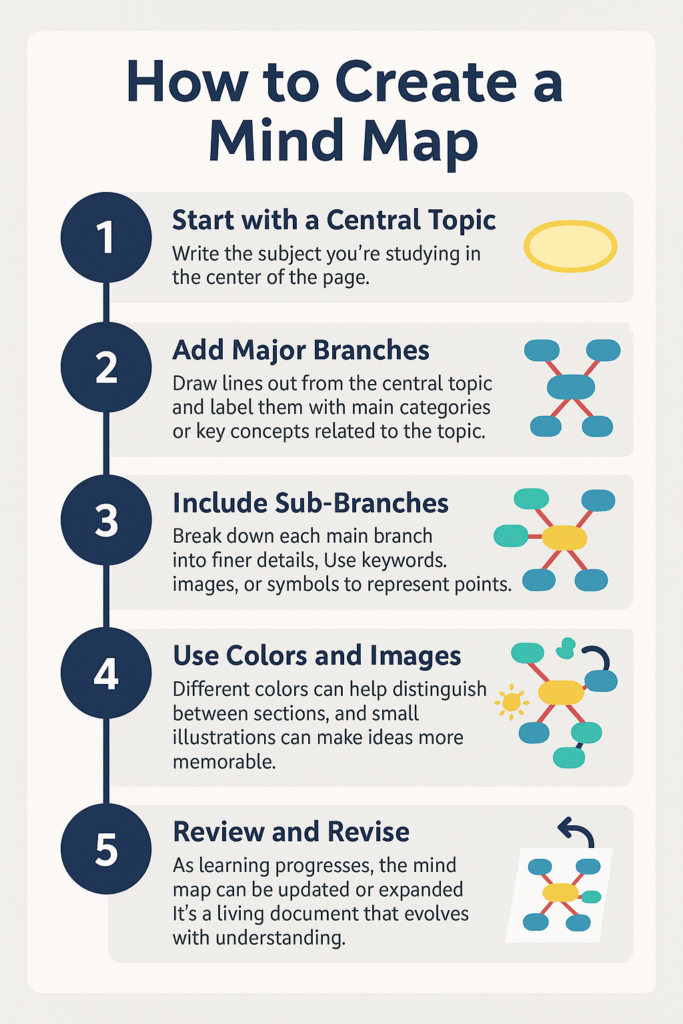
Creating a mind map is simple and customizable:
- Start with a Central Topic – Write the subject you’re studying in the center of the page. This could be anything from “World History” to “Marketing Strategies.”
- Add Major Branches – Draw lines out from the central topic and label them with main categories or key concepts related to the topic.
- Include Sub-Branches – Break down each main branch into finer details. Use keywords, images, or symbols to represent important points.
- Use Colors and Images – Different colors can help distinguish between sections, and small illustrations can make ideas more memorable.
- Review and Revise – As learning progresses, the mind map can be updated or expanded. It’s a living document that evolves with understanding.
Using Mind Maps for Learning
Mind map learning can be applied in many contexts — studying for exams, planning a project, summarizing a book, or preparing a presentation. It helps condense large amounts of information into an organized and visually appealing format.
Whether using pen and paper or a digital tool like MindMeister, XMind, or SimpleMind, learners can personalize their maps to suit their style and goals.
Final Thoughts
Mind mapping is more than a note-taking method — it’s a dynamic tool for thinking, learning, and creating. With practice, anyone can harness the power of mind map learning to master new subjects with clarity and confidence.


